INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER SCIENCE
2. The Era of Mobile Computing and Artificial Intelligence (Present - Future):
The rise of smartphones and tablets: These powerful mobile devices have become an extension of ourselves, offering computing capabilities on the go.
Artificial Intelligence (AI): Advancements in AI are changing the landscape of computing. AI algorithms are now capable of complex tasks like facial recognition, natural language processing, and even self-driving cars.
Computer: A computer is basically defined as a tool or machine used for processing data to give required information.
A computer is an electronic device (machine) that accepts inputs (data), performs calculations, processes and manipulates your inputs, stores and outputs them (displays).
It is capable of:
- taking input data through the keyboard (input unit),
- storing the input data in a diskette, hard disk or other medium,
- processing it in the central processing unit (CPU) and
- giving out the result (output) on the screen or the Visual Display Unit (VDU).
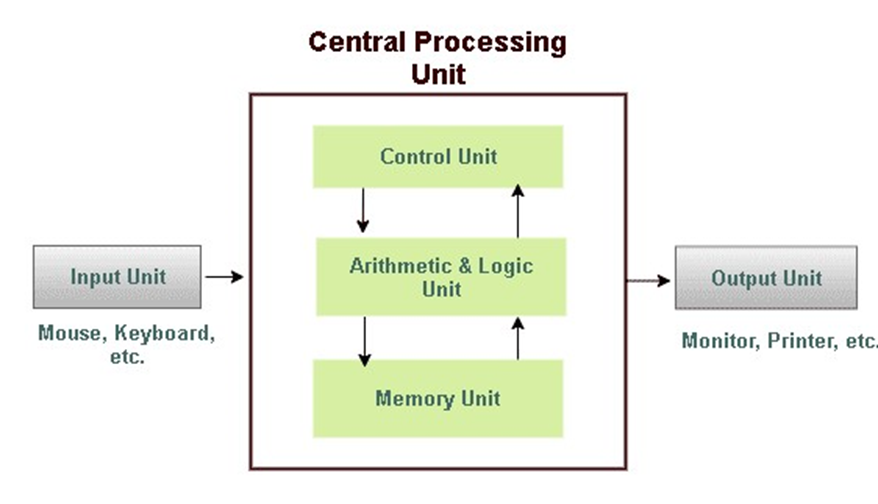
Fig. 1: A schematic block to diagram of a computer
Characteristics of a Computer
1) Speed: The computer can manipulate large data at incredible speed and response time can be very fast.
2) Accuracy: Its accuracy is very high and its consistency can be relied upon. Errors committed in computing are mostly due to human rather than technological weakness. There are in-built errors detecting schemes in the computer.
3) Storage: It has both internal and external storage facilities for holding data and instructions. This capacity varies from one machine to the other. Memories are built up in K (Kilo) modules where K=1024 memory locations.
4) Automatic: Once a program is in the computer‘s memory, it can run automatically each time it is opened. The individual has little or no instruction to give again.
5) Reliability: Being a machine, a computer does not suffer human traits of tiredness and lack of concentration. It will perform the last job with the same speed and accuracy as the first job every time even if ten million jobs are involved.
6) Flexibility: It can perform any type of task once it can be reduced to logical steps. Modern computers can be used to perform a variety of functions like on-line processing, multi- programming, real time processing etc.