COMPUTER
| Site: | Newgate University Minna - Elearning Platform |
| Course: | Introduction to Computer Science |
| Book: | COMPUTER |
| Printed by: | Guest user |
| Date: | Tuesday, 2 December 2025, 7:49 PM |
1. computer
A computer is an electronic device (machine) that accepts inputs (data), performs calculations, processes and manipulates your inputs, stores and outputs them (displays).
Computer can be divided into three parts
1. Software
2. Hardware
3. Human ware
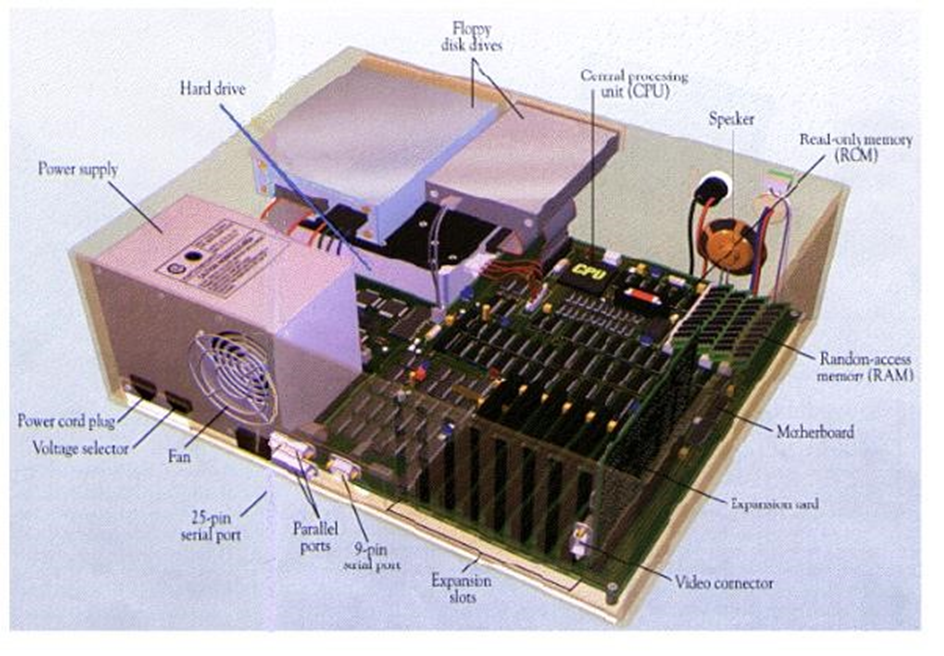
Computer Hardware
The term hardware refers to all of the physical devices and tangible components of a computer. A computer is not one single device, but a system of devices that all work together. Computer is divided into four units
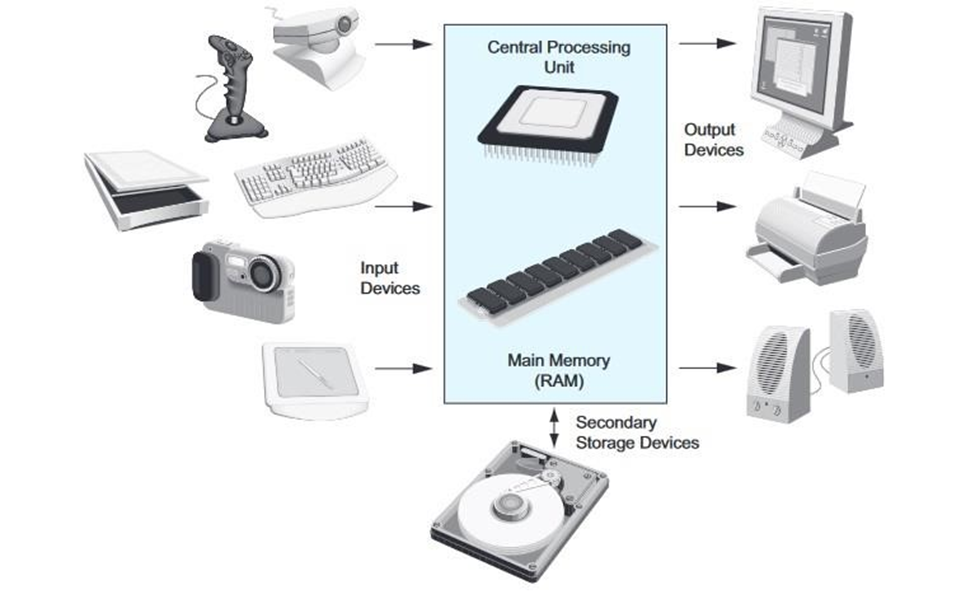
2. Computer is divided into four units
FIGURE
2
3. TYPICAL COMPONENTS OF COMPUTER SYSTEM
Logical Organization of a Computer
The logical organization of a computer is based on its definition.
The computer hardware comprises of the following Units:
• Input unit
• The central processing unit (CPU) (Control unit and Arithmetic & logic unit)
• Memory unit
• Output unit
Input Unit: means by which data is entered into the computer that includes all input device or means through which computer accepts data from users via the input devices. Examples include the keyboard, mouse, joystick, trackball and scanner.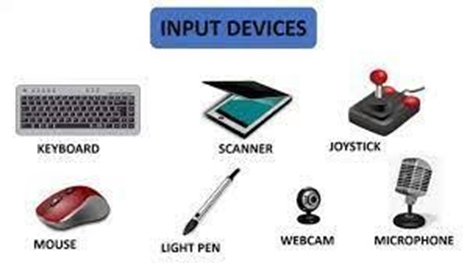
KEYBOARD: We use a pencil or pen to write in a book. We use chalk or a marker to write on the board in class. We can‘t use any of these to write on a computer, so we use the keyboard to enter information and instructions to the computer.
KEYS OF KEYBOARD
Computer keyboards include keys that are designed to perform specific tasks. These keys enable the user to perform complex tasks easily when using the application. For example, many applications use a function key to access online help for the user.
Types of Computer Keyboard
There are four major types of Computer Keyboard used worldwide depending on their size and numbers of keys are QWERTY, AZERTY, DVORAK and QWERTZ
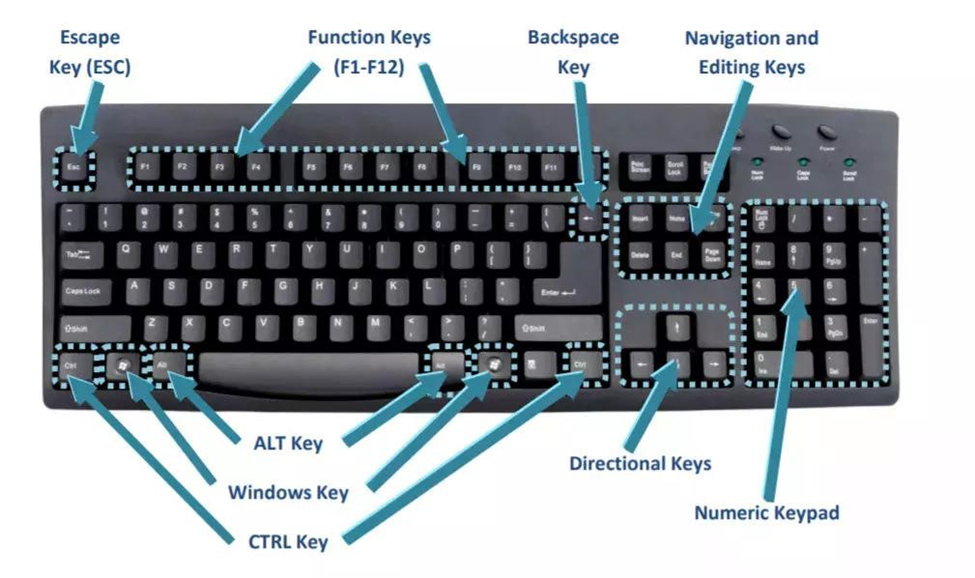 Keyboard keys consist of
Keyboard keys consist of
• Alphabetic keys
• Numerical keys
• Symbols
• Functional keys
• Extra keys
Alphabetic keys contain alphabets from A-Z & a-z
Numerical keys contain numbers 0-9
Symbols keys contain many symbols like!, @, #, $, % etc
Functional keys contain f1-f12, design for special purpose will discuss latter.
Extra keys contain Esc, Alt, Ctrl, Backspace, Enter etc
4. Output Unit
means by which data is displayed on the
computer screen to the user. An output unit is responsible for presenting
information or results to the user in a human-readable or perceivable form.
Examples are Monitor, Printer, Speaker, Plotter, Projector etc.

CPU (Central Processing Unit)
CPU is made up of ALU and CU. Both control (control unit or CU) and arithmetic & logic unit (ALU) combine called as Central Processing Unit (CPU). The Processor Unit (CPU)
It is the brain of a computer system.
All major calculation and comparisons are made inside the CPU and it is also responsible for activation and controlling the operation of other unit.
This unit consists of two major components that are arithmetic logic unit (ALU) and control unit (CU).
Central Processing Unit (CPU) consists of the following features − CPU is considered as the brain of the computer.
• CPU performs all types of data processing operations.
• It stores data, intermediate results, and instructions (program).
• It controls the operation of all parts of the computer.

• Memory or Storage Unit
• Control Unit
ALU(Arithmetic Logic Unit)5. Memory or Storage Unit
This unit can store instructions, data, and intermediate results. This unit supplies information to other units of the computer when needed. It is also known as internal storage unit or the main memory or the primary storage or Random Access Memory (RAM).
Its size affects speed, power, and capability. Primary memory and secondary memory are two types of memories in the computer. Functions of the memory unit are − It stores all the data and the instructions required for processing.
• It stores intermediate results of processing.
• It stores the final results of processing before these results are released to an output device.
• All inputs and outputs are transmitted through the main memory.
Control Unit
This unit controls the operations of all parts of the computer but does not carry out any actual data processing operations.
And the control unit of a CPU controls the entire operation of a computer. It also controls all devices such as memory, input/output devices connected to the CPU.
CU fetches instructions from memory, decodes the instruction, interprets the instruction to know what the task are to be performed and sends suitable control signals to the other components to perform for the necessary steps to execute the instruction.
Functions of this unit are −
• It is responsible for controlling the transfer of data and instructions among other units of a computer.
• It manages and coordinates all the units of the computer.
• It obtains the instructions from the memory, interprets them, and directs the operation of the computer.
• It communicates with Input /Output devices for transfer of data or results from storage.
• It does not process or store data.
ALU (Arithmetic Logic Unit)
This unit consists of two subsections namely,
• Arithmetic Section
• Logic Section
Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU)
Here arithmetic logic unit performs all arithmetic operations such as addition, subtraction, multiplication and division. It also uses logic operation for
- Arithmetic Section
Function of arithmetic section is to perform arithmetic operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. All complex operations are done by making repetitive use of the above operations. - Logic Section
Function of logic section is to perform logic operations such as comparing, selecting, matching, and merging of data.
The information fed through the input unit is stored in computer's memory for processing and the final result stored in memory can be recorded or display on the output medium.
Memory Unit
Memory unit is an essential component of a digital computer. It is where all data intermediate and final results are stored.
The data read from the main storage or an input unit are transferred to the computer's memory where they are available for processing.
This memory unit is used to hold the instructions to be executed and data to be processed. Two types of storage unit are primary and secondary storage unit.
Primary/Main Storage Unit
Primary memory has direct link with input unit and output unit. It stores the input data, calculation result.
Secondary/Auxiliary Storage Unit
The primary storage is not able to store data permanently for future use. So some other types of storage technology is required to store the data permanently for long time, it is called secondary or auxiliary storage.
6. DIFFERENCE BETWEEN PRIMARY MEMORY AND SECONDARY MEMORY
S/N. Primary memory Secondary memory
1. Primary memory is temporary. Secondary memory is permanent.
Primary memory is directly accessible by Secondary memory is not directly
2.
Processor/CPU. accessible by the CPU.
Nature of Parts of Primary memory
3. varies, RAM- volatile in nature. ROM- It‘s always Non-volatile in nature. Non-volatile.
Primary memory devices are more Secondary memory devices are less
4. expensive than secondary storage expensive when compared to primary devices. memory devices.
The memory devices used for primary The secondary memory devices are
5. memory are semiconductor memories. magnetic and optical memories.
Secondary memory is also known as Primary memory is also known as Main
6. External memory or Auxiliary memory or Internal memory. memory.
Examples: RAM, ROM, Cache memory, Examples: Hard Disk, Floppy Disk,
7. PROM, EPROM, Registers, etc. Magnetic Tapes, etc.
7. PERIPHERAL DEVICES
A peripheral device is generally defined as any auxiliary device such as a computer mouse or keyboard that connects to and works with the computer in some way.
Peripheral devices, often referred to as peripherals, are hardware components or devices that are connected to a computer or other digital device to provide additional functionality, input, or output. These devices extend the capabilities of the main computer system and allow users to interact with, control, or exchange data with the computer. Peripheral devices are typically not an integral part of the central processing unit (CPU) or the core system components but serve specific purposes. Other examples of peripherals are expansion cards, graphics cards, image scanners, tape drives, microphones, loudspeakers, webcams, and digital cameras
Common examples of peripheral devices include:
1. Input Devices: These devices allow users to input data or commands into the computer.
Examples include:
- Keyboards: Used for typing text and entering commands.
- Mice: Pointing devices used for navigating the graphical user interface. o Scanners: Used to digitize physical documents and images. o Digital Cameras: Capture and input digital images and videos.
- Microphones: Capture audio input for voice recognition or audio recording.
2. Output Devices: These devices provide information or results from the computer to the user. Examples include: o Monitors: Display the visual output of the computer, including text, images, and videos.
Printers: Produce physical copies of digital documents. o Speakers: Output audio for music, videos, and system sounds.8. PERIPHERAL DEVICES
A peripheral device is generally defined as any auxiliary device such as a computer mouse or keyboard that connects to and works with the computer in some way.
Peripheral devices, often referred to as peripherals, are hardware components or devices that are connected to a computer or other digital device to provide additional functionality, input, or output. These devices extend the capabilities of the main computer system and allow users to interact with, control, or exchange data with the computer. Peripheral devices are typically not an integral part of the central processing unit (CPU) or the core system components but serve specific purposes. Other examples of peripherals are expansion cards, graphics cards, image scanners, tape drives, microphones, loudspeakers, webcams, and digital cameras
Common examples of peripheral devices include:
1. Input Devices: These devices allow users to input data or commands into the computer.
Examples include:
- Keyboards: Used for typing text and entering commands.
- Mice: Pointing devices used for navigating the graphical user interface. o Scanners: Used to digitize physical documents and images. o Digital Cameras: Capture and input digital images and videos.
- Microphones: Capture audio input for voice recognition or audio recording.
2. Output Devices: These devices provide information or results from the computer to the user. Examples include: o Monitors: Display the visual output of the computer, including text, images, and videos.
Printers: Produce physical copies of digital documents. o Speakers: Output audio for music, videos, and system sounds.9. INTERNAL COMPONENTS OF A COMPUTER