EXPLORING THE COMPUTING LANDSCAPE
| Site: | Newgate University Minna - Elearning Platform |
| Course: | Introduction to Computer Science |
| Book: | EXPLORING THE COMPUTING LANDSCAPE |
| Printed by: | Guest user |
| Date: | Tuesday, 2 December 2025, 9:57 PM |
Description
IDENTIFY DIFFERENT AREAS AND PROGRAMS WITHIN THE VAST FIELD OF COMPUTING.
Table of contents
- 1. IDENTIFY DIFFERENT AREAS AND PROGRAMS WITHIN THE VAST FIELD OF COMPUTING.
- 2. Learn about job specializations for computing professionals.
- 3. Other Specializations:
- 4. Data Science & Machine Learning:
- 5. COMPONENTS OF A WINDOWS DESKTOP
- 6. MICROSOFT WORD (MS WORD)
- 7. H0W TO LAUNCH MICROSOFT WORD
- 8. FEATURES OF MICROSOFT OFFICE
- 9. DRAG & DROP METHOD
- 10. INSERTING FEATURES TO A DOCUMENT
1. IDENTIFY DIFFERENT AREAS AND PROGRAMS WITHIN THE VAST FIELD OF COMPUTING.
IDENTIFY DIFFERENT AREAS AND PROGRAMS WITHIN THE VAST FIELD OF COMPUTING.
Software Development:
Front-End Development
Back-End Development
Full-Stack Development
Mobile Development (Android, iOS)
Web Development
Game Development
Embedded Systems Development
Software Engineering (various specializations)
User Interface (UI) / User Experience (UX) Design
Data Science & Machine Learning v Data Science
Machine Learning Engineering
Data Analysis
Data Visualization
Business Intelligence (BI)
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Systems Engineering & IT:
Systems Engineering
Network Engineering
Security Engineering
Database Administration (DBA)
Cloud Computing
IT Support
Network Security
Information Security
Cybersecurity (Specializations):
Information Security v Network Security
Application Security
Cloud Security
Digital Forensics
Security Architecture
Blockchain Technology:
Blockchain Development
Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT)
Smart Contracts Development
Cryptography
Internet of Things (IoT): v IoT Engineering
Embedded Systems Design
Wireless Sensor Networks
Data Analytics for IoT
Robotics:
Robotics Engineering
Artificial Intelligence for Robotics
Machine Learning for Robotics
Robot Control Systems
Quantum Computing:
Quantum Computing Science v Quantum Algorithms
Quantum Information Theory
Quantum Machine Learning
Natural Language Processing (NLP): v Computational Linguistics
Machine Translation
Text ‗Summarization
Sentiment Analysis v Speech Recognition
Bioinformatics:
Computational Biology
Genomics
Proteomics
Bioinformatics Algorithms
2. Learn about job specializations for computing professionals.
The world of computing offers a diverse range of job specializations, each requiring a unique skillset and focusing on specific areas. Here's an overview of some popular specializations for computing professionals:
Software Development:
Specializations: This broad category encompasses various roles like:
- Front-End Developer: Focuses on the user interface (UI) and user experience (UX) of web applications, using languages like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript.
- Back-End Developer: Builds the server-side logic of web applications, ensuring data processing and communication with databases. Languages like Java, Python, and PHP are common choices.
- Full-Stack Developer: Possesses skills in both front-end and back-end development, capable of handling the entire application development cycle.
- Mobile Developer: Creates applications for smartphones and tablets, using platforms like Android or iOS and languages like Kotlin or Swift.
Data Science & Machine Learning:
Specializations: This field involves extracting insights from data. It includes roles like:
- Data Scientist: Analyzes data to uncover patterns and trends, using statistics, machine learning, and programming languages like Python (with libraries like NumPy, Pandas).
- Machine Learning Engineer: Builds and implements machine learning models for tasks like prediction or classification. Expertise in algorithms, data processing, and cloud platforms is essential.
- Data Analyst: Cleans, organizes, and analyzes data to generate reports and communicate findings to stakeholders. Skills in SQL for database querying and data visualization tools like Tableau are valuable.
Systems Engineering & IT:
- Specializations: This area deals with computer systems and networks. It includes roles like:
- Systems Engineer: Designs, implements, and maintains computer systems, ensuring smooth operation and troubleshooting technical issues.
- Network Engineer: Plans, builds, and manages computer networks, ensuring data security and reliable network connectivity.
3. Other Specializations:
• Web Developer: Creates websites and web applications, using languages like HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and back-end technologies like PHP or Node.js.
• Database Administrator (DBA): Manages and maintains databases, ensuring data integrity, security, and performance. Knowledge of SQL and database management systems (e.g., MySQL, Oracle) is crucial.
• Software Engineer: A broad role that often involves designing, developing, testing, and deploying software systems.
• Game Developer: Creates video games, using programming languages like C++, C#, and scripting languages like Lua.
Choosing Your Path:
The best job specialization depends on your interests, skills, and career goals. Consider these factors when making your choice:
• Areas of Interest: What aspects of computing excite you the most? Data analysis, building applications, or network security?
• Skillset: What are you good at? Are you analytical, creative, or detail-oriented?
• Job Market: Research the demand and career outlook for different specializations.
Remember, this is not an exhaustive list, and the computing field is constantly evolving. There are many exciting specializations emerging, so keep exploring to find the perfect fit for you!
Deep Dive into Computing Job Specializations:
The world of computing offers a plethora of career paths, each requiring a unique skillset and focusing on specific areas. Here's a detailed exploration of some popular specializations:
Software Development:
• Front-End Developer: These are the artists and architects of the web. They craft the user interface (UI), the visual elements users interact with, and the user experience (UX), ensuring a smooth and enjoyable interaction. Languages like HTML (structure), CSS (styling), and JavaScript (interactivity) are their tools of choice. They might also use frameworks like React or Angular for complex web applications.
• Back-End Developer: The behind-the-scenes heroes, back-end developers build the server-side logic of web applications, handling data processing, storage (databases like MySQL or PostgreSQL), and communication between different parts of the system. Languages like Java (enterprise applications), Python (versatile and popular for web development), PHP (widely used for web development), and Node.js (event-driven for real-time applications) are commonly used.
• Full-Stack Developer: The ultimate utility players, full-stack developers possess expertise in both front-end and back-end development. They can handle the entire application development cycle, from building the UI to implementing the server-side logic. This requires a broader skillset, including languages from both areas and potentially knowledge of cloud platforms like AWS or Azure.
• Mobile Developer: App enthusiasts rejoice! Mobile developers create applications specifically for smartphones and tablets. They specialize in platforms like Android (using Kotlin or Java) or iOS (using Swift), working within the guidelines and limitations of these mobile operating systems.
4. Data Science & Machine Learning:
• Data Scientist: Data is the new gold, and data scientists are the prospectors. They mine valuable insights from massive datasets using statistical methods, machine learning algorithms, and programming languages like Python (with libraries like NumPy for numerical computing and Pandas for data manipulation). They might also use visualization tools like Tableau to communicate their findings effectively.
• Machine Learning Engineer: Building intelligent systems is the realm of machine learning engineers. They translate algorithms from research papers into real-world applications. They have a strong foundation in algorithms, data processing techniques, and cloud platforms like Google Cloud Platform (GCP) or Amazon Web Services (AWS) to train and deploy these models.
• Data Analyst: The data detectives, data analysts clean, organize, and analyze data to answer specific business questions. They often use SQL (Structured Query Language) to interact with databases and extract data. Tools like Tableau or Power BI allow them to create compelling data visualizations to communicate insights to stakeholders who may not be technical experts.
Systems Engineering & IT:
• Systems Engineer: The system architects, systems engineers design, implement, and maintain computer systems. They ensure all components work together seamlessly, troubleshoot technical issues, and perform upgrades when necessary. They possess a broad understanding of hardware, software, networking concepts, and virtualization technologies.
• Network Engineer: The network guardians, network engineers plan, build, and manage computer networks. They ensure reliable data flow within an organization or across the internet. They configure network devices like routers and switches, implement security measures like firewalls, and monitor network performance to identify and resolve any issues.
• Security Engineer: The cybersecurity warriors, security engineers safeguard computer systems and networks from cyberattacks. They understand security protocols, conduct vulnerability assessments to identify weaknesses in systems, and perform penetration testing to simulate attacks and identify potential breaches. Knowledge of security tools and incident response procedures is essential.
Beyond the Basics:
• Web Developer: A broader term, web developers encompass both front-end and backend development skills to create websites and web applications. They use a combination of languages like HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and back-end technologies like PHP or Node.js.
• Database Administrator (DBA): The data custodians, DBAs manage and maintain databases, ensuring data integrity, security, and performance. They have in-depth knowledge of SQL and database management systems like MySQL or Oracle. They are responsible for backups, user management, and ensuring smooth database operations.
• Software Engineer: This broad role encompasses designing, developing, testing, and deploying software systems. They might specialize in a particular area like embedded systems, system software, or enterprise applications. The specific skillset will vary depending on the specialization.
Game Developer: Bringing video games to life is the job of game developers. They use programming languages like C++ or C# for high-performance graphics and scripting languages like Lua for game logic. They might also work on 3D modeling, animation, and sound design to create immersive gaming experiences.5. COMPONENTS OF A WINDOWS DESKTOP
The basic components of the windows desktop are:
4. ICON
5. TASKS BAR
6. BACKGROUND
ICON
An Icon in windows is a small picture or object that represents a file, program, web page or command prompt. Mostly the Icon are related to the function of the item that it represents
TASK BAR
A taskbar is a virtual device on the desktop that typically shows the user which applications (tasks) are currently active and running it is usually found at the bottom of the desktop, but it depends user‘s modification.
BACKGROUND
A background is also called DESKTOP. It is the area where Icons and windows are displayed.
WORD PROCESSING: can be define as the process of using software to create, edit, view, store, retrieve, format and print textual documents such as letter head papers, memo and other documents.
A WORD PROCESSOR is software that is used for word processing. Examples of word processors (word processing packages)
(1) Microsoft word (2) WordStar (3) Word perfect (4) word pro (5) Corel word perfect
(6) Lotus note (7) perfect writer (8) MultiMate advantage (9) professional writer
ADVANTAGES OF WORD PROCESSOR
I. Word processing software produce error-free document II. It avoids retyping of documents
III. It permits in printing multiple copies of the document once the document is created
IV. It permits in checking spelling and grammar automatically
V. It helps in choosing the most appropriate word in a context
VI. Facility to generate beautifully formatted documents
VII. It supports mail merging
VIII. It has additional facilities such as inserting of objects from other files and linking of documents through hypertext
THE USES OF WORD PROCESSOR
Word processor can be used to do the following:
✔ To create books
✔ Articles
✔ Newsletter
✔ Resumes
✔ Notes
✔ Assignments
✔ Birthday cards
✔ Invitation cards
✔ Lectures scripts
✔ Letterhead samples
✔ Bills
✔ Cash memo
✔ Joining letters
✔ Receipt
✔ To create calendar
✔ Report
✔ Brochure
✔ Application form
✔ eBook
Use as translator6. MICROSOFT WORD (MS WORD)
Microsoft word is a word processor designed by Microsoft Corporation USA. It is the most common word processor today because of its special features. It comes in a software suite called Microsoft office. Some versions of Microsoft office are: MS office 2000, MS office 2003, MS office 2007, MS 2010.MS 2013, MS 2016, MS 2019,2021
(Microsoft word) comes in a software suite called Microsoft office which comprises of
1. Microsoft word
2. Power point
3. Excel
4. Outlook
5. Publisher
6. Groove
Microsoft access etc7. H0W TO LAUNCH MICROSOFT WORD
There are three methods in launching Microsoft word
Method 1
1. Take the mouse pointer to start button on the task bar. Click the left mouse button.
2. Move the pointer to programs. You will notice another menu coming up to the right.
3. In that menu identify where Microsoft word is placed. Move the cursor horizontally to come out of the programs.
Move into the rectangular area meant for the MS word. Click the left mouse button there. The computer will start MS-word.Method 2
Double click on the Microsoft word icon on the desktop
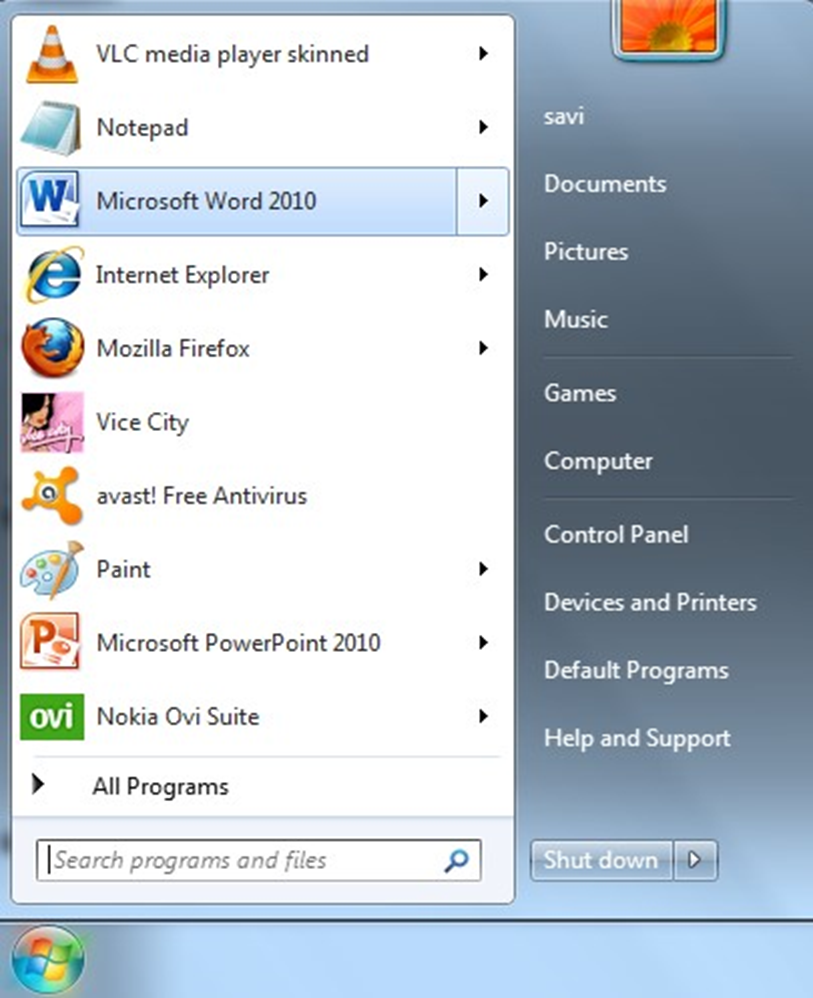
Method 2
Double click on the Microsoft word icon on the desktop

Method 3
Besides these two methods other methods for opening word are:
Using Run Command.
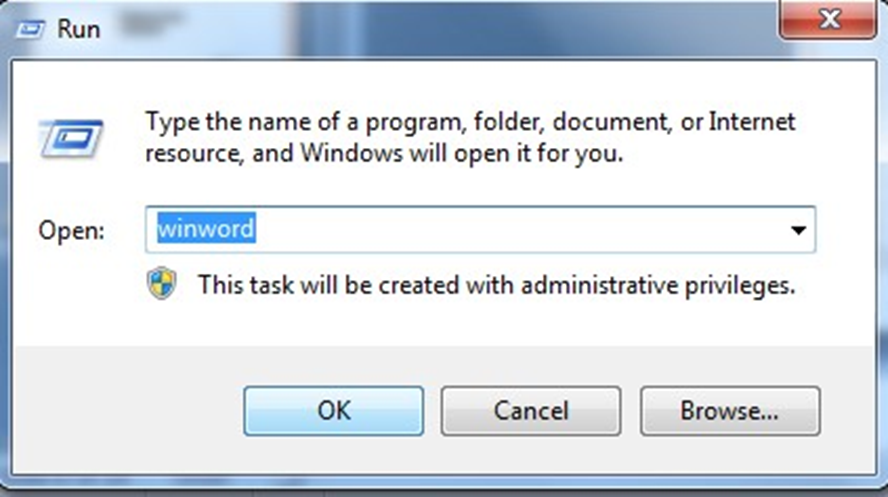
Using DOS: Specify the absolute path to open WINWORD.EXE title. After writing the absolute path the MS-Word will open up.
Microsoft word has different features. Some of the features are Opening a Document, Editing a Document, Formatting a Document, Inserting a Document, Saving a Document, Retrieving an existing Document, The office button, Menu Bar, Title Bar, Minimize button ,Maximize button, Closing a Document etc.
8. FEATURES OF MICROSOFT OFFICE
⮚ The office Button- It‘s located in the upper left corner of MS word. Whenever you click on the button, you will see the basic command available on the file menu, open, save and print etc
⮚ Menu Bar- This contains the Home page (edit) insert, page layout, reference, mailing, review, view.

⮚ Title Bar – It gives information about the name of the package as well as the name of the document you are working on.
⮚ Minimize Button- It‘s used to hide current document/ work.
⮚ Maximize Button- The button give command to a document to restore previously minimize document or to enlarge window below.
⮚ Close Button- Its use to close document.
⮚ The Horizontal Ruler- This enable a user scale a document horizontally
⮚ The vertical Ruler- This enable a user document vertically
⮚ Status Bar- contains information about a document, examples are : The page currently being viewed by the user, number of words in a document
⮚ Creating a New Document/ opening of New Document
Anytime you load Microsoft word, a new document is opened by default. To open a new document
● Click on the office button
● Select new from displayed options
● Select blank document from the dialog box
● Click on create button
NOTE- A blinking cursor will appear in the text area called the insertion point, then follow the cursor by first deleting the initial text before you enter the text or the name you want to give the new document.
The top banner of features on Word is referred to as the Ribbon. The Ribbon includes the Ribbon tabs (just below the top blue banner) and specific commands for each Tab. Clicking any tab will take you to the Ribbon commands for that heading.
⮚ Opening of Existing Document
● Click on the office button
● Select open from the displayed options
● Select the drive or directory where the document is located
● Select the document from the dialog box
● Click open button
⮚ Editing a Document
The editing features in MS word are
1. Copy, cut and paste
2. Format painter
3. Thesaurus
4. Finding and replace
5. Go to
6. Spelling & Grammar
7. Word count
CUT- Cut feature is use to remove information from document
PASTE- Is a feature use to place the information been cut or copy from same or different document.
COPY- Copying a document or portion of a document means duplicating the document.
N.B: The original document will still remain while the duplicate of it will be found in a new location.
METHODS OF COPYING A DOCUMENT
|
⮚ |
Shortcut method |
|
⮚ |
Keyboard method |
|
⮚ |
Drag & drop method |
|
⮚ |
Ribbon bar method |
|
⮚ |
Right mouse method |
SHORTCUT METHOD PROCEDURE)
✔ Highlight the portion of a document to be copied
✔ Right click on the highlighted text
✔ Select copy
✔ Position the insertion point in a new location
✔ Right click in an empty space
✔ Select paste
KEYBOARD METHOD (PROCEDURE)
✔ Highlight the text to be copied in the Document
✔ Press the ctrl + C to copy
✔ Position the cursor on the insertion point
Press the key ctrl + V to paste9. DRAG & DROP METHOD
DRAG & DROP METHOD
✔ Highlight the text to be copied
✔ Hold down the ctrl key as you drag the highlights to a new location
✔ Release the mouse button
RIBBON BAR METHOD
✔ Highlight the portion of the document to be copied
✔ Click on the Home ribbon
✔ Click copy on the clipboard
✔ Position the insertion point in a new location
✔ Click on the paste from the Home Ribbon (clipboard)
NOTE- To cut a document means to move the document from its original location to a different location.
All the steps involved when copying a document are equally applicable with the cut method, but the only difference is that, instead of selecting copy, you just need to select cut before pasting the document.
FIND AND REPLACE
Whenever a mistakes is made all over a document. For example mistakenly typed fred instead of fried, the find and replace feature help locate the errors and quickly replace them with the expected text. To apply the find and replace feature in a document:
● Click on the Home ribbon
● Click on the find icon on the drop down arrow and select find.
● Click on the replace Tab
● Type the error text in the find what text box and the corrected text in the Replace with text box
● Click on replace all if you want it to do an entire document correction or Replace if you want it one after the other.
● Click cancel button to abort operations.
GOTO
This is a quick navigation command. It is used to move to a specified location within a document without having to scroll through almost the entire pages.
SPELLING AND GRAMMAR
They check whether a document is error free both spelling and grammar.
FORMATTING A DOCUMENT chalk cheek
Formatting a document is processing of making a document presentable, which entails the following
❖ Font : A font format contains the following
1. Font Face- This is the text outlook of a document, which can be Arial, Times New Roman, freestyle script, Tahoma etc.
2. Font size- This is the text sizes of the document which ranges from 8-72
3. Font Style- This is the effects on the text, examples are bold, italic, regular, bold italic, underline.
4. Font colour- This is the colour effect on the text such as rd, green, blue etc.
5. Font effect- This display other effect on text such as strike through, subscript, superscript, change case etc.
6. Character spacing- This display different characteristic of spacing that can be applied on the text. Examples, expanded or condensed, kerning etc.
❖ Paragraph- This feature determines the distances between texts and lines
1. Indent and spacing- This feature creates a text with spacing before or after. examples are alignment indentation and spacing
❖ Bullets and Numbering- This format displays how a list should appear.
✔ Bullets- This is a way of using a picture in form of icons to illustrate list. ✔ Numbering- This is the way of using number to list items.
The numbering of items can either be Roman or Arabic Numerals10. INSERTING FEATURES TO A DOCUMENT
These include MS word embedded features and external features that can be extracted into a document. They include:
I. Tables
II. Pictures or Clip Art
III. Shapes
IV. Header & Footer
V. Page Number
VI. Text Box
VII. Word Art
VIII. Drop Cap
IX. Symbols
SAVING A DOCUMENT
Best practice demands that we save our document before we begin creating texts; this is because of power failure or unforeseen circumstances.
You can save your documents in two different ways, which includes
● SAVE (Require no password)
● SAVE AS ( This type of saving require you to save your documents using passwords in some windows like Windows XP)
PRINT PREVIEW
It is ideal to preview all documents before any print operations this will determines if the document is intact as it should be.
SHORT CUT KEYS
|
|
Keys |
Meaning |
|
Ctrl +A |
|
To Highlight all |
|
Ctrl + B |
|
To Bold |
|
Ctrl + C |
|
To Copy |
|
Ctrl + D |
|
For Font |
|
Ctrl + E |
|
To align to the centre |
|
Ctrl + F |
|
To Find |
|
Ctrl + G |
|
GOTO |
|
Ctrl + H |
|
To replace |
|
Ctrl + I |
|
Italic |
|
Ctrl + J |
|
Justify |
|
Ctrl + k |
|
To insert hyperlink |
|
Ctrl + L |
|
Alignment to the left |
|
Ctrl +M |
|
Indent |
|
Ctrl + N |
|
Open a New Document |
|
Ctrl + O |
|
Brings up a browse dialog and allows you to select a file to open |
|
Ctrl + P |
Prints a document |
|
|
Ctrl + Q |
To change line spacing |
|
|
Ctrl + R |
Align text Right |
|
|
Ctrl + S |
To Save |
|
|
Ctrl + U |
To Underline |
|
|
Ctrl + V |
To paste copied document |
|
|
Ctrl + W |
To close currently open document |
|
|
Ctrl + X |
To cuts (removes) a selected documents |
|
|
Ctrl + Y |
To redo |
|
|
Ctrl + Z |
To Undo last command |
|