SPREADSHEET
| Site: | Newgate University Minna - Elearning Platform |
| Course: | Introduction to Computer Science |
| Book: | SPREADSHEET |
| Printed by: | Guest user |
| Date: | Tuesday, 2 December 2025, 10:05 PM |
1. SPREADSHEET
A spreadsheet is a computer application for organization, analysis and storage of data in tabular form. A spreadsheet is a computer program that can capture, display and manipulate data arranged in rows and columns.
A spreadsheet is a computer application for organization, analysis and storage of data in tabular form. Spreadsheets were developed as computerized analogs of paper accounting worksheets. The program operates on data entered in cells of a table. A spreadsheet consists of a table of cells arranged into rows and columns and referred to by the X and Y locations. X locations, the columns, are normally represented by letters, "A", "B", "C", etc., while rows are normally represented by numbers, 1, 2, 3, etc.
A single CELL can be referred to by addressing its row and column, "C10" for instance.
Spreadsheets have the concept of a range, a group of cells, normally contiguous. Spreadsheet applications, several spreadsheets, often known as worksheets or simply sheets, are gathered together to form a workbook. A workbook is physically represented by a file, containing all the data for the book, the sheets, and the cells with the sheets. Worksheets are normally represented by tabs that flip between pages, each one containing one of the sheets, although Numbers changes this model significantly.
Spreadsheets share many principles and traits of databases, but spreadsheets and databases are not the same things. A spreadsheet is essentially just one table, whereas a database is a collection of many tables with machine-readable semantic relationships between them2. Uses of a spreadsheet
Although spreadsheets are used with anything containing numbers, the uses of a spreadsheet are almost endless. Below are some other popular uses of spreadsheets.
Finance
Spreadsheets are ideal for financial data, such as your checking account information, budgets, taxes, transactions, billing, invoices, receipts, forecasts, and any payment system.
Forms
Form templates can be created to handle inventory, evaluations, performance reviews, quizzes, time sheets, patient information, and surveys.
School and grades
Teachers can use spreadsheets to track students, calculate grades, and identify relevant data, such as high and low scores, missing tests, and students who are struggling.
Lists
Managing a list in a spreadsheet is a great example of data that does not contain numbers, but still can be used in a spreadsheet. Great examples of spreadsheet lists include telephone, to-do, and grocery lists.
Sports
Spreadsheets can keep track of your favorite player stats or stats on the whole team. With the collected data, you can also find averages, high scores, and statistical data. Spreadsheets can even be used to create tournament brackets and help track fantasy football stats.
Examples of Spreadsheet
1. Microsoft Excel,
2. Lotus 1-2-3
3. Google Sheets
4, Quattro Pro
6. StarOffice
Kingsoft Office3. EXCEL
Microsoft Excel is a program that provide worksheets comprised of rows and columns. Textual data can be stored in the workbook similarly to a Microsoft Word table, but the power of Excel is its ability to perform to complicated mathematical calculations.
The Excel Worksheet (Spreadsheet) and Workbook
An Excel worksheet, or spreadsheet, is a two-dimensional grid with columns and rows. The column names are letters of the alphabet starting with A, and the rows are numbered chronologically starting with the number one. The cells in the first row are A1, B1, C1, and so on. And the cells in the first column are A1, A2, A3, and so on. These are called cell names or cell references.
WORKBOOK & WORKSHEET
A workbook is a spreadsheet program file that you create in Excel. A workbook contains one or more worksheets.
A worksheet (also known as a spreadsheet) consists of cells in which you can enter and calculate data. The cells are organized into columns and rows. A worksheet is always stored in a workbook.
A workbook is a collection of worksheets or spreadsheets. When the Excel program is opened, a workbook opens with three blank worksheets. The names of the worksheets are displayed on tabs at the bottom of the Excel window.
What is a Cell?
Cell: A cell is a rectangular area formed by the intersection of a column and a row. Cells are identified by the Cell Name (or Reference, which is found by combining the Column Letter with the Row Number.
For example the cell in Column "C" in Row "3" would be cell C3. How are rows and columns labeled?
In all spreadsheet programs, including Microsoft Excel, rows are labeled using numbers (e.g., 1 to 1,048,576). All columns are labeled with letters from A to Z, then with two letters. For example, after the letter Z, the next column is AA, AB, AC, ..., AZ and then incrementing to BA, BB, BC, etc., to the last column XFD (16,384 columns)
The Name Box is located in the area above Column A, and displays the cell reference of the selected cell - the cell where the cursor is resting. In our spreadsheet above, the selected cell is C2. Notice that the column letter (C) and the row number (2) change color.
The beginning of the Formula Bar can be seen in the area above Column D on our worksheet. The Formula Bar displays the contents of the selected cell.
Moving from Cell to Cell
The arrow keys can be used to move left, right, up, and down from the current cell. Press the Enter key to move to the cell immediately below the current cell, and press the Tab key to move one cell to the right.
Selecting Cells
There are a variety of ways to select cells in an Excel spreadsheet:
To select one cell, click in the cell.
To select one or more rows of cells, click on the row number(s).
To select one or more columns of cells, click on the column letter(s).
To select a group of contiguous cells, click in a corner cell and, with the left mouse button depressed, drag the cursor horizontally and/or vertically until all of the cells you want selected are outlined in black.
To select multiple cells that are not contiguous, press and hold the Ctrl key while clicking in the desired cells.
To select every cell in the worksheet, click in the upper right corner of the worksheet to the left of "A."4. How do I enter data in a spreadsheet?
In a spreadsheet, data is entered in one or more cells. To enter data in a cell, follow the steps below.
1. Click the cell where you want to enter data.
2. Start typing the data using your keyboard. The data is automatically entered in the selected cell.
or
1. Click the cell where you want to enter additional data.
2. Click in the formula bar, located between the Ribbon and all cells, where you want to start entering the additional data.
3. Type the data using your keyboard. The data is automatically entered in the selected cell.
Entering Data into Cells
To enter data into a cell, just click in the cell and begin typing. What you type also displays in the Formula Bar. When entering dates, Excel defaults to the current year if the year portion of the date is not entered.
Working with Worksheets (Spreadsheets)
Viewing, Renaming, Inserting, and Deleting Worksheets
Worksheet tabs are found in the bottom left area of the workbook. To view a worksheet, click on its tab.
If the workbook window is not wide enough to display all of the tabs, use the arrows to the left of the tabs to navigate left or right, or right-click on any of the arrows and select the tab from the list that displays.
To rename a spreadsheet, right-click on the spreadsheet tab, select Rename from the context menu, and type a new name. Or, double-click on the worksheet tab and type a new name. To insert a worksheet, right-click on a worksheet tab and select Insert from the menu. Excel always inserts the spreadsheet to the left of the current worksheet.
To delete a worksheet, right-click on the worksheet tab and select Delete from the context menu.
Moving Worksheets (Spreadsheets)
Sometimes we want our spreadsheets to be arranged in a different order. To move a worksheet in the same workbook, right-click on the tab of the source worksheet and click "Move or Copy." In the Move or Copy window, click the name of the worksheet that you want the sheet to be inserted before, and click OK.
To move a spreadsheet to a new workbook, right-click on the tab of the source spreadsheet and click "Move or Copy." In the Move or Copy window, click the drop-down arrow under ―To Book:‖ and click (new book). Excel removes the worksheet from the existing workbook and opens a new workbook containing the moved worksheet.
To move a worksheet to another existing workbook, we recommend copying the worksheet as instructed below, and then deleting the original sheet when the worksheet has been successfully pasted.
Using cut and paste is an option, but if something happens to the PC before pasting occurs, a valuable worksheet could be lost.
Copying Worksheets (Spreadsheets)
Rather than start from scratch, it is often easier to copy, and then modify, an existing worksheet. To copy a worksheet in the same workbook, right-click on the tab of the source worksheet and click "Move or Copy." In the Move or Copy window, check the ―create a copy‖ box, click the name of the spreadsheet that you want the sheet to be inserted before, and click OK.
To copy a worksheet into a new workbook, right-click on the tab of the source worksheet and click "Move or Copy." In the Move or Copy window, click the drop-down arrow under ―To
Book:‖ and click (new book). Excel opens a new workbook containing the copied spreadsheet.
To copy a worksheet from one workbook to another existing workbook, right-click the top left corner cell to select all cells and click Copy. Open the other Excel workbook, find an empty worksheet, right-click the top left corner cell to select all cells, and click Paste. Return to the first worksheet and press ESC to remove the animated border.5. Basic Terms in Excel
1. Formulas
In Excel, a formula is an expression that operates on values in a range of cells or a cell. For example, =A1+A2+A3, which finds the sum of the range of values from cell A1 to Cell A3.
2. Functions
Functions are predefined formulas in Excel. They eliminate laborious manual entry of formulas while giving them human-friendly names. For example: =SUM (A1:A3). The function sums all the values from A1 to A3.
Five Time-saving Ways to Insert Data into Excel
When analyzing data, there are five common ways of inserting basic Excel formulas. Each strategy, however, comes with an advantage over the other. Therefore, before diving further into the main formulas,
1. Simple insertion: Typing a formula inside the cell
Typing a formula in a cell or the formula bar is the most straightforward method of inserting basic Excel formulas. The process usually starts by typing an equal sign, followed by the name of the function.
Excel is quite intelligent in that when you start typing the name of the function, a pop-up function hint will show. It‘s from this list you‘ll select your preference. However, don‘t press the Enter key. Instead, press the Tab key so that you can continue to insert other options. Otherwise, you may find yourself with an invalid name error, often as ‗#NAME?‘. To fix it, just re-select the cell, and go to the formula bar to complete your function.
Note that pressing F2 while hovered over a cell allows you to edit the cells‘ formula.
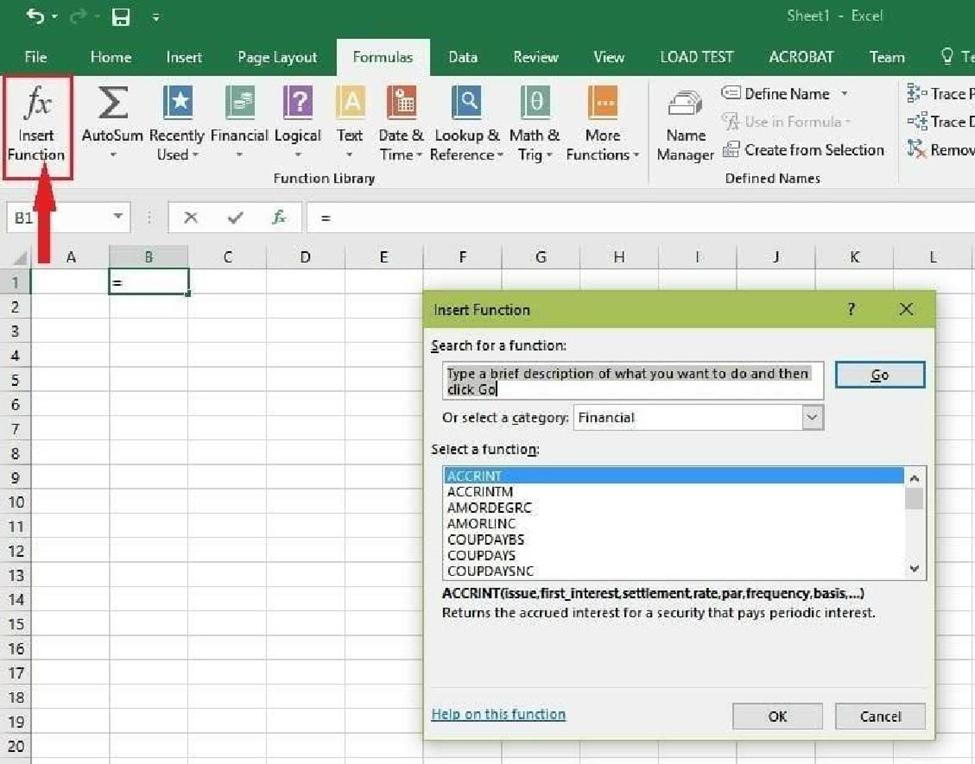
6. Using Insert Function Option from Formulas Tab
1. Using Insert Function Option from Formulas Tab
If you want full control of your functions insertion, using the Excel Insert Function dialogue box is all you ever need. To achieve this, go to the Formulas tab and select the first menu labeled Insert Function. The dialogue box will contain all functions you need to complete your analysis. The Excel shortcut to insert a function is ALT + M + F. The Corporate Finance Institute Excel
2. Selecting a Formula from One of the Groups in Formula Tab
The option is for those who want to delve into their favorite functions quickly. To find this menu, navigate to the Formulas tab and select your preferred group. Click to show sub-menu filled with a list of functions. From there, you can select your preference. However, if you find your preferred group is not on the tab, click on the More Functions option – probably it‘s just hidden there.
The Excel formula shortcuts are the following:
Recently used: ALT + M + R
Financial: ALT + M + I
Logical: ALT + M + L
Text: ALT + M + T
Date & Time: ALT + M + E
Lookup & Reference: ALT + M + O
Math & Trig: ALT + M + G
More Function: ALT + M + Q The Corporate Finance Institute Excel
4. Using AutoSum Option
For quick and everyday tasks, AutoSum is your go-to option. So, navigate to the Home tab, in the far-right corner, click the AutoSum option. Then click the caret to show other hidden formulas. This option is also available in the Formulas tab first option after the Insert Function option.
Alternatively, the Autosum Excel function can be accessed by typing ALT + the = sign in a spreadsheet and it will automatically create a formula to sum all the numbers in a continuous range.
Step 1: Place the cursor below the column of numbers you want to sum (or to the left of the row of numbers you want to sum).
Step 2: Hold down the Alt key and then press the equals = sign while still holding Alt.
Step 3: Press Enter.
5. Quick Insert: Use Recently Used Tabs
If you find re-typing your most recent formula a monotonous task, then use the Recently Used menu. It‘s on the Formulas tab, a third menu option just next to AutoSum. The Corporate Finance Institute Excel