Thyroid and Adrenal Glands
Completion requirements
The thyroid and adrenal glands are two essential endocrine organs that regulate a wide range of physiological processes crucial for survival, growth, metabolism, and adaptation to stress.
While the thyroid gland primarily controls the rate of energy metabolism and protein synthesis, the adrenal glands coordinate the body’s stress response, electrolyte balance, and metabolic adjustments through hormonal secretion.
Together, they exemplify how the endocrine system maintains homeostasis through finely tuned hormonal interactions and feedback control mechanisms
1. The Thyroid Gland
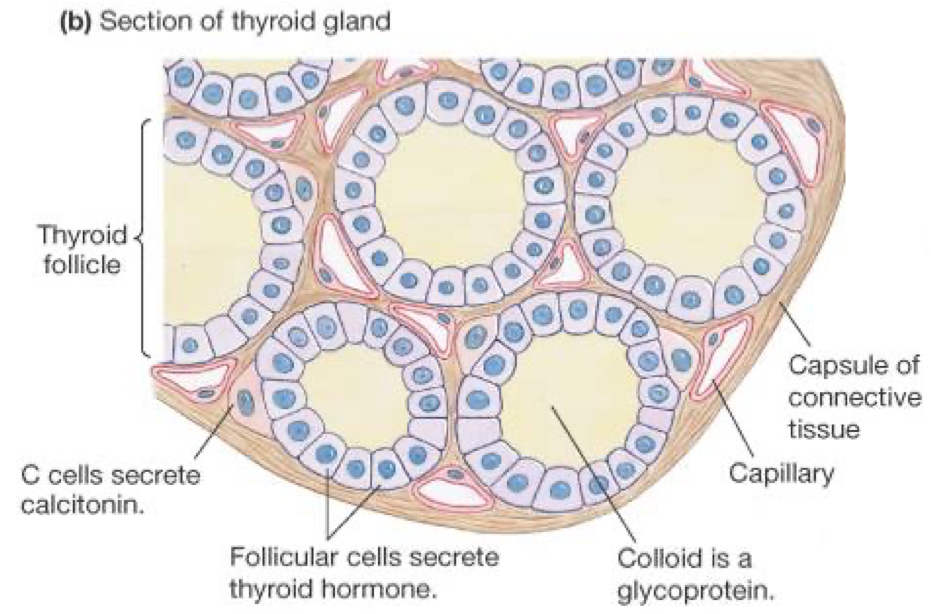
1.1. Structure and Function of the Thyroid Gland
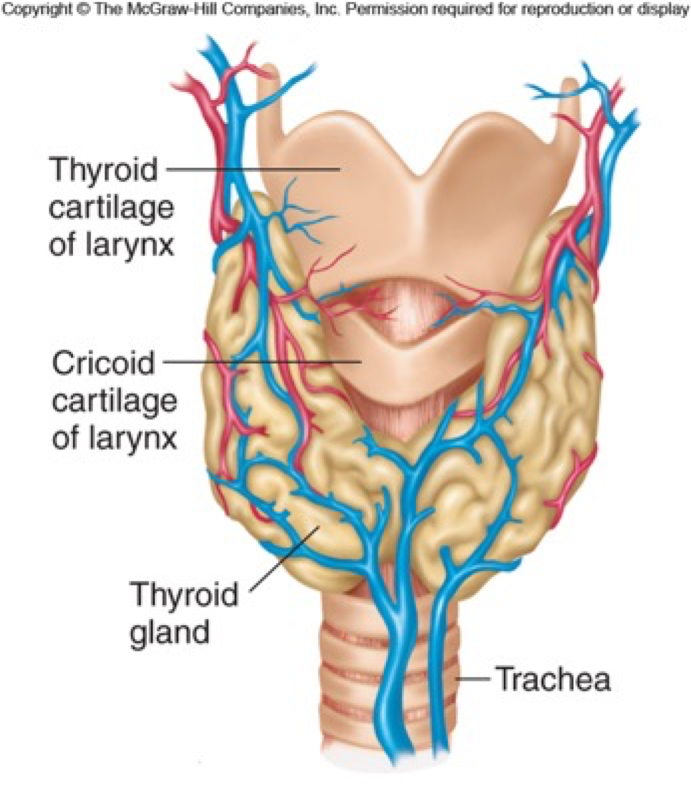
- Location: Anterior neck, below larynx, butterfly-shaped.
- Microscopic
structure:
- Follicles – spherical units filled with colloid (thyroglobulin).
- Follicular cells – synthesize thyroid hormones (T₃, T₄).
- Parafollicular (C) cells – secrete calcitonin.
- Thyroglobulin is made by the follicular cells.
- Thyroglobulin acts as the thyroid hormone synthesis and storage site
- Thyroid follicles actively accumulate iodine and secrete it into the colloid.